Point of Care Testing (POCT)
Information on the various Point of Care Testing (POCT) programmes and initiatives undertaken by UK NEQAS to ensure safe and effective result generation, irrespective of where, when or by whom the test is performed.
Sections

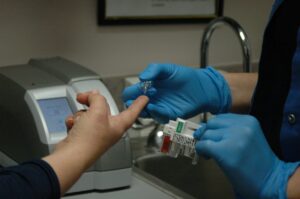 Rapid growth in the use of Point of Care Testing (POCT), also known as near-patient testing (NPT), has occurred in many areas of diagnostic analysis.
Rapid growth in the use of Point of Care Testing (POCT), also known as near-patient testing (NPT), has occurred in many areas of diagnostic analysis.
Tests that were once an offshoot of laboratory analysis have expanded to occupy a substantial proportion of diagnostic testing, not only for the monitoring of, for example, glucose levels in diabetes and prothrombin time / international normalised ratio (PT/INR) in oral anticoagulant control, but also in standalone diagnostic tests, including molecular and genetic testing.
With the spread of POCT, there has also been a parallel increase in the provision of External Quality Assessment (EQA) for POCT.
Provision of specimens for assay/platform evaluation
EQA specimens are prepared for distribution to participants according to predetermined timetables which are planned many months in advance. UK NEQAS specimens are designed to be suitable for “real-time” analysis, supplying material that closely resembles patient samples.
To meet the demands of Point of Care Testing (POCT) EQA, these samples are produced in fixed quantities, potentially with limited shelf life, and are often derived from finite source material.
UK NEQAS Centres frequently receive requests from point of care diagnostic service providers for previous or surplus EQA specimens for the purpose of assay/platform evaluation. Unfortunately, due to limited specimen stability, availability, and commutability issues, it may not always be possible to accommodate such requests.
Individual UK NEQAS centres can provide further information regarding their policy for supporting participants with provision of surplus EQA specimens for assay/platform evaluation.
UK NEQAS offers the following EQA programmes for Point of Care Testing (POCT):
UK NEQAS Blood Coagulation
- Activated Clotting Time (ACT): This test is typically used to monitor heparin therapy, especially high doses used during as well as pre-and post-surgical procedures.
- D-Dimer: Following formation of a blood clot, fibrinolytic activity results in degradation products, including cross-linked ‘D’ fragments of fibrin (D-Dimer). Results below a cut-off level when used with a clinical pre-test probability score can be used to exclude the condition venous thromboembolism (VTE).
- INR Testing: (CoaguChek XS series, CoaguChek Pro II, i-STAT, LumiraDx): Warfarin is an anticoagulant given to patients to prevent a thrombotic event. The INR test is used to monitor the anticoagulation levels of patients on warfarin therapy.
- Thromboelastometry and Thromboelastography: Viscoelastic methods for monitoring haemostasis, where the rheological conditions of blood samples under test are measured and recorded, analysing the process of clot formation, stabilisation and subsequent degradation.
UK NEQAS Blood Transfusion Laboratory Practice
- D-Typing: To determine whether anti-D Ig prophylaxis is required following termination of pregnancy, to prevent sensitisation to the D antigen.
UK NEQAS Cardiac Markers
- B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP): To help detect, diagnose, and evaluate the severity of congestive heart failure (CHF).
- Cardiac Troponin I: To determine if a patient has had heart muscle damage of which heart attack is one cause; to determine if angina is worsening.
- Cardiac Troponin T: To determine if a patient has had heart muscle damage of which heart attack is one cause; to determine if angina is worsening.
- CKMB: Is a legacy test which can be used to distinguish between skeletal muscle and heart muscle damage; sometimes to determine if a patient has had a heart attack.
- Myoglobin: To determine whether muscle has been injured or to help diagnose conditions associated with muscle damage.
UK NEQAS Clinical Chemistry (Birmingham Quality)
- Clinical Chemistry: A range of tests to fulfil the needs of POCT users, both hospital based and in the community, for Clinical Chemistry tests. The testing repertoire, in terms of scope and frequency we offer, is only limited to what the end users require, but this must be approved by Birmingham Quality. Please contact Birmingham Quality about your specific requirements.
- Glycated Haemoglobins: We have whole-blood based material to assist in the diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes.
- Urine Dipsticks: Urine Dipsticks (Urinalysis) measure multiple constituents such as pH, glucose, protein, bilirubin, blood, ketones, nitrites, and leucocytes to assess kidney and urinary tract infections, diabetes, and liver function. Results from both visual interpretation and automated urine dipstick readers are accepted.
UK NEQAS Edinburgh Peptide Hormones
- Pregnancy Testing: The determination of Urinary hCG confirms or excludes pregnancy.
UK NEQAS Haematology
- Hb: To monitor the performance of participants using point of care, single parameter instruments for the measurement of haemoglobin concentration.
- PX: To monitor the performance of participants using the PixCell Hemoscreen point-of-care analyser for the measurement of FBC parameters, including the 5-part leukocyte differential.
UK NEQAS Immunology, Immunochemistry & Allergy (IIA)
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP): To identify the presence of inflammation and to reduce antibiotic prescribing in patients without a clinical diagnosis of pneumonia.
UK NEQAS Microbiology
- Cryptococcal Antigen: Detection of the presence or absence of Cryptococcal antigens in serum.
- HIV: To provide EQA for laboratory and non-laboratory settings that use POCT devices to screen for HIV. Participants are required to determine the presence (reactive) or absence (negative) of HIV 1 and HIV 2 Ab by POCT devices.
- Hepatitis B serology: Testing for markers of Hepatitis B infection (HBsAg, HBc Ab, HBc IgM etc.) in serum. Suitable for point of care testing devices as well as laboratory diagnostics assays.
- Hepatitis C serology: Testing for Hepatitis C Ag/Ab in serum. Suitable for point of care testing devices as well as laboratory diagnostics assays.
- Hepatitis E detection: Testing for Hepatitis E IgM, IgG and RNA in serum. Suitable for point of care testing devices as well as laboratory diagnostics assays.
- HIV Point of Care: Screening for HIV-1/2 Ag/Ab in serum with point of care testing devices.
- Respiratory viruses Point of Care: Testing for Influenza A/B, RSV A/B and/or SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid and/or Ag using point of care testing devices. Specimens are supplied in VTM and are suitable for swab-based assays.
- Syphilis serology: Testing for markers of T. pallidum infection (reagin, treponemal antibodies – IgM, IgG) in serum. Suitable for point of care testing devices as well as laboratory diagnostics assays.
- Urinary Antigens: Detection of Legionella pneumophila and Streptococcus pneumoniae antigens in urine
- Viral Gastroenteritis: Testing for Norovirus, Rotavirus and (3) enteric Adenovirus (types 40 and 41) nucleic acid and/or Ag. Specimen are supplied in a freeze-dried format and require resuspension. Suitable for point of care testing devices as well as laboratory diagnostics assays.
UK NEQAS Parasitology
- Malaria Rapid: To test for Malaria (in the UK this is performed by Laboratories).